The stock market can be a complex and intimidating place, especially for beginners. There are many terms and concepts that can be confusing, making it difficult to understand how things work. This blog post aims to demystify some of the most basic stock market terms, so you can feel more confident navigating the investment world. 1. P/E Ratio (Price-to-Earnings Ratio) The P/E ratio is a metric used to compare a company's stock price to its earnings per share (EPS). It essentially tells you how much you are paying for each rupee of a company's earnings. A higher P/E ratio can indicate that a stock is more expensive relative to its earnings, while a lower P/E ratio can indicate that a stock is cheaper. However, it is important to remember that the P/E ratio is just one factor to consider when evaluating a stock, and it should be compared to similar companies within the same industry. 2. Dividends Dividends are a portion of a company's profits that are paid out to its sharehol...
The financial market is constantly evolving, and new financial instruments are being introduced to meet the changing demands of investors. Two such instruments that have gained popularity in recent years are futures and options.
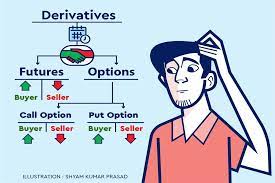
Futures and options are derivatives, which means their value is derived from an underlying asset, such as a stock, index, commodity, or currency. Both futures and options are contracts that give the holder the right to buy or sell the underlying asset at a specified price and at a specific date in the future.
Futures:
Futures are contracts where the buyer agrees to purchase an asset at a specified price and date in the future. Futures are used by investors to hedge against price changes in the underlying asset. For example, if a farmer expects the price of wheat to fall in the future, he can sell wheat futures to lock in a price for his crop.
Futures can also be used for speculation. If an investor believes that the price of an asset will rise in the future, he can buy futures contracts and profit from the price increase. Futures contracts are traded on exchanges, and the price of the contract is determined by supply and demand.
Options:
Options are contracts that give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a specified price and date in the future. Unlike futures, options give the holder the right to buy or sell the asset, but not the obligation to do so.
Options can be used for hedging or speculation. An investor can buy a call option if he expects the price of an asset to rise in the future, and he can buy a put option if he expects the price of an asset to fall in the future. If the price of the asset moves in the direction the investor predicted, he can exercise the option and profit from the price movement.
Options are also used for hedging. For example, a company that needs to buy raw materials in the future can buy call options on the raw materials to lock in a price.
The Future of Futures and Options:
Futures and options have been around for decades, but their popularity has increased in recent years due to the growth of online trading platforms and the availability of low-cost trading fees. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that the popularity of futures and options will continue to grow.
One area where futures and options may see growth is in the cryptocurrency market. As cryptocurrencies become more widely accepted, there may be a need for futures and options contracts to hedge against price volatility.
Another area where futures and options may see growth is in the renewable energy market. As more companies look to reduce their carbon footprint, there may be a need for futures and options contracts to hedge against fluctuations in renewable energy prices.
Options are also used for hedging. For example, a company that needs to buy raw materials in the future can buy call options on the raw materials to lock in a price.
The Future of Futures and Options:
Futures and options have been around for decades, but their popularity has increased in recent years due to the growth of online trading platforms and the availability of low-cost trading fees. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that the popularity of futures and options will continue to grow.
One area where futures and options may see growth is in the cryptocurrency market. As cryptocurrencies become more widely accepted, there may be a need for futures and options contracts to hedge against price volatility.
Another area where futures and options may see growth is in the renewable energy market. As more companies look to reduce their carbon footprint, there may be a need for futures and options contracts to hedge against fluctuations in renewable energy prices.
Conclusion:
Futures and options are financial instruments that are used by investors for hedging and speculation. Futures are contracts where the buyer agrees to purchase an asset at a specified price and date in the future, while options give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a specified price and date in the future.
As the financial market continues to evolve, it is likely that futures and options will become even more popular. Whether it is in the cryptocurrency market, the renewable energy market, or another area, futures and options will continue to provide investors with a way to manage risk and profit from price movements.


Comments
Post a Comment