The stock market can be a complex and intimidating place, especially for beginners. There are many terms and concepts that can be confusing, making it difficult to understand how things work. This blog post aims to demystify some of the most basic stock market terms, so you can feel more confident navigating the investment world. 1. P/E Ratio (Price-to-Earnings Ratio) The P/E ratio is a metric used to compare a company's stock price to its earnings per share (EPS). It essentially tells you how much you are paying for each rupee of a company's earnings. A higher P/E ratio can indicate that a stock is more expensive relative to its earnings, while a lower P/E ratio can indicate that a stock is cheaper. However, it is important to remember that the P/E ratio is just one factor to consider when evaluating a stock, and it should be compared to similar companies within the same industry. 2. Dividends Dividends are a portion of a company's profits that are paid out to its sharehol...
Key financial ratios like earnings per share (EPS), price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, and return on equity (ROE) can be used to evaluate a company's financial health and performance. These ratios are calculated by analyzing a company's financial statements, which include the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
Here is a brief explanation of each of the ratios you mentioned:
- Earnings per share (EPS): This is a measure of a company's profitability. It is calculated by dividing the company's net income by the number of outstanding shares of common stock. EPS can be compared with industry averages to determine if a company is performing well relative to its peers.
- Price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio: This ratio measures the value of a company's stock relative to its earnings. It is calculated by dividing the market price per share by the earnings per share. A high P/E ratio can indicate that investors have high expectations for a company's future growth, while a low P/E ratio may suggest that investors are pessimistic about the company's prospects.
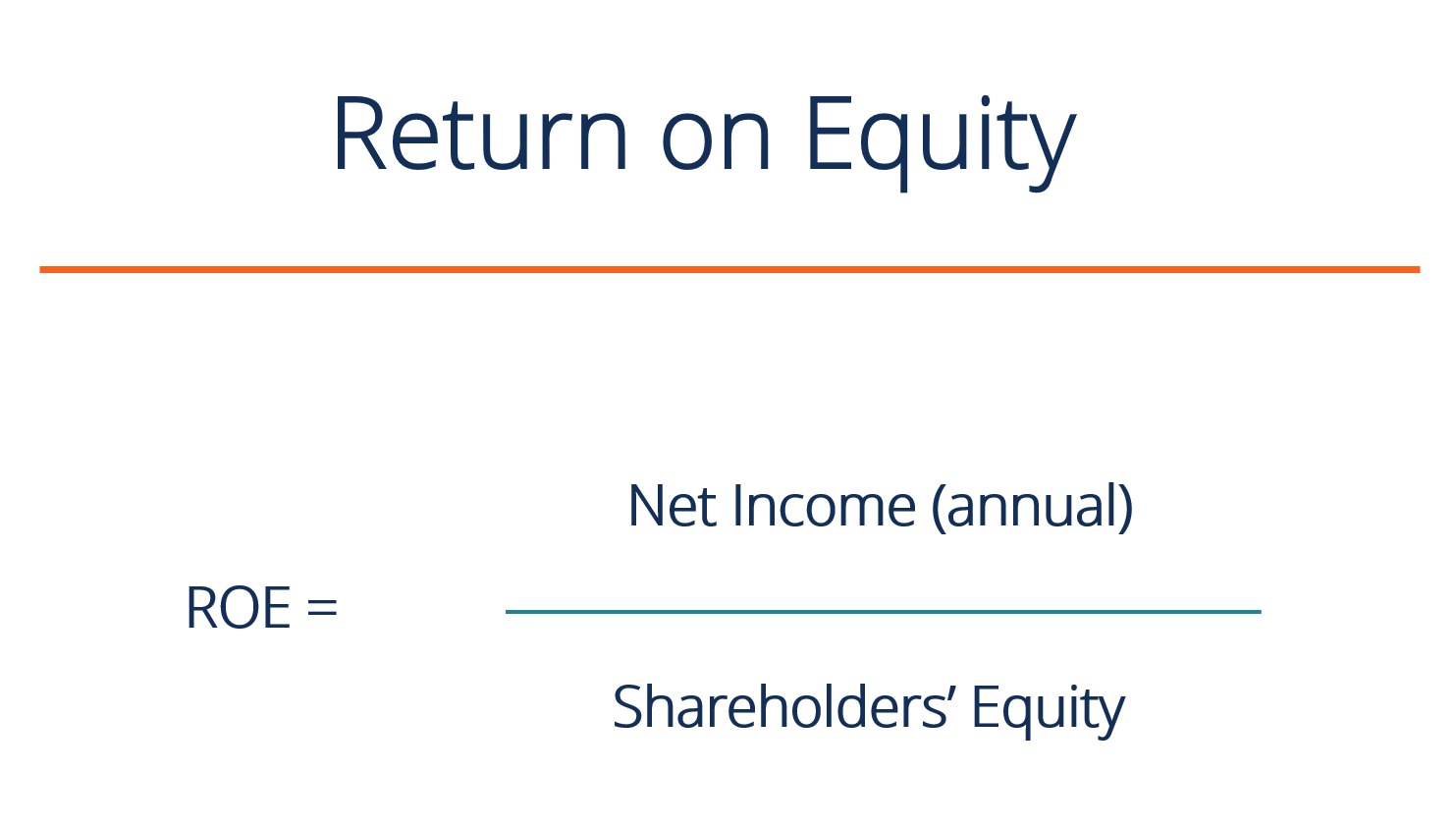
- Return on equity (ROE): This ratio measures a company's ability to generate profits from shareholders' equity. It is calculated by dividing the company's net income by its average shareholder equity. A high ROE indicates that a company is effectively using its shareholder equity to generate profits, while a low ROE may suggest that a company is not using its resources efficiently.
By comparing these ratios to industry averages, investors and analysts can gain insights into a company's financial health and performance. However, it is important to keep in mind that these ratios should be used in conjunction with other financial metrics and qualitative factors, such as the company's competitive landscape and management team, to make informed investment decisions.


Comments
Post a Comment